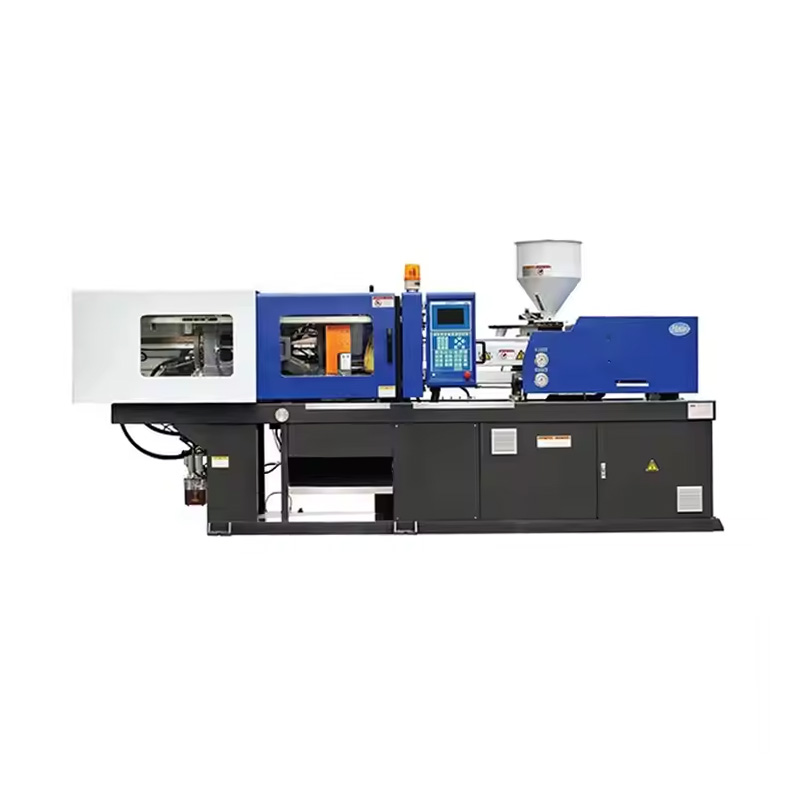
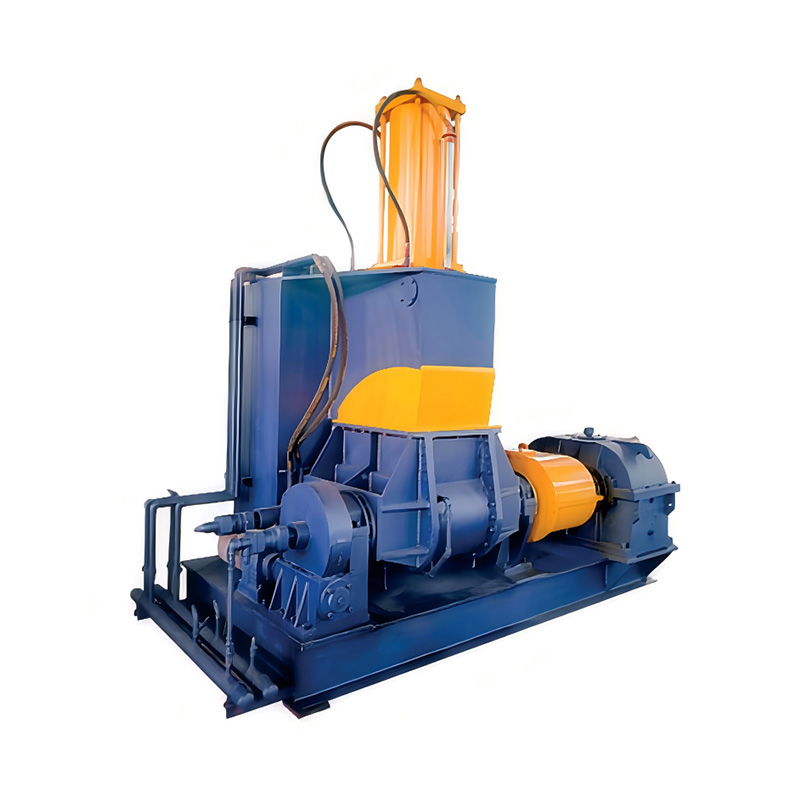
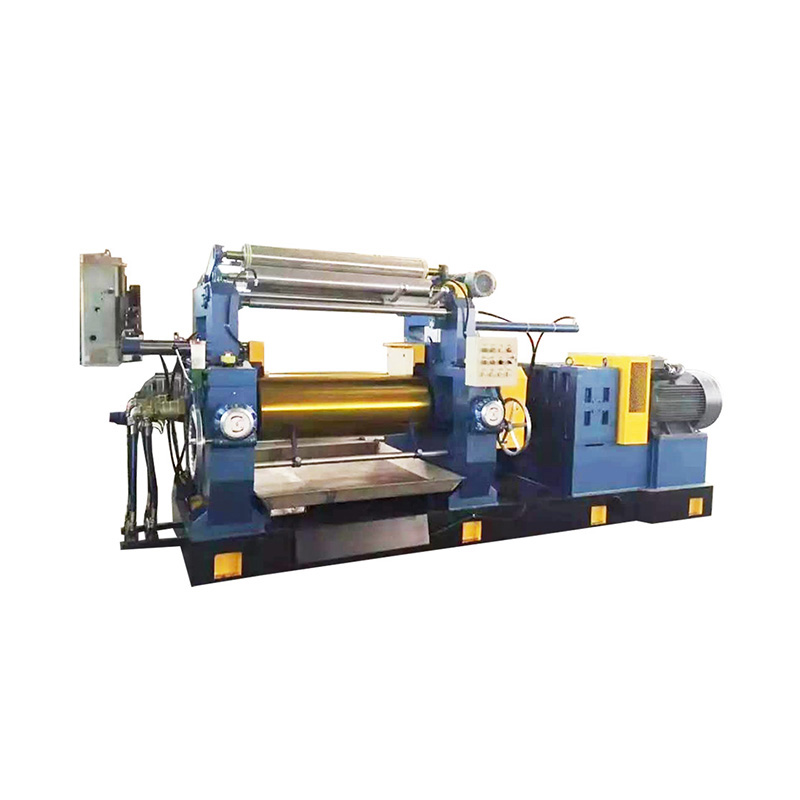
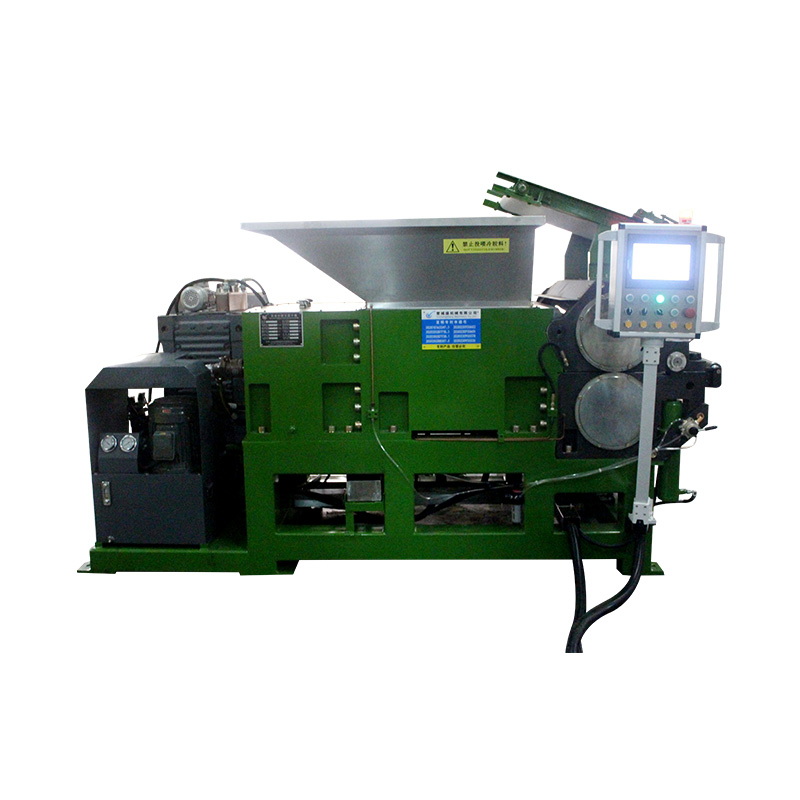
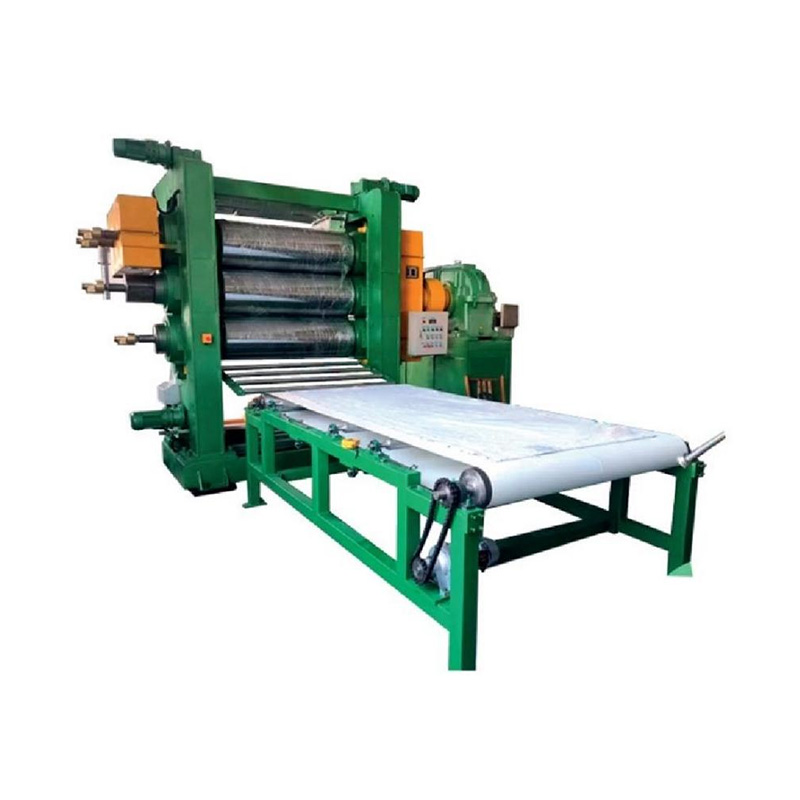
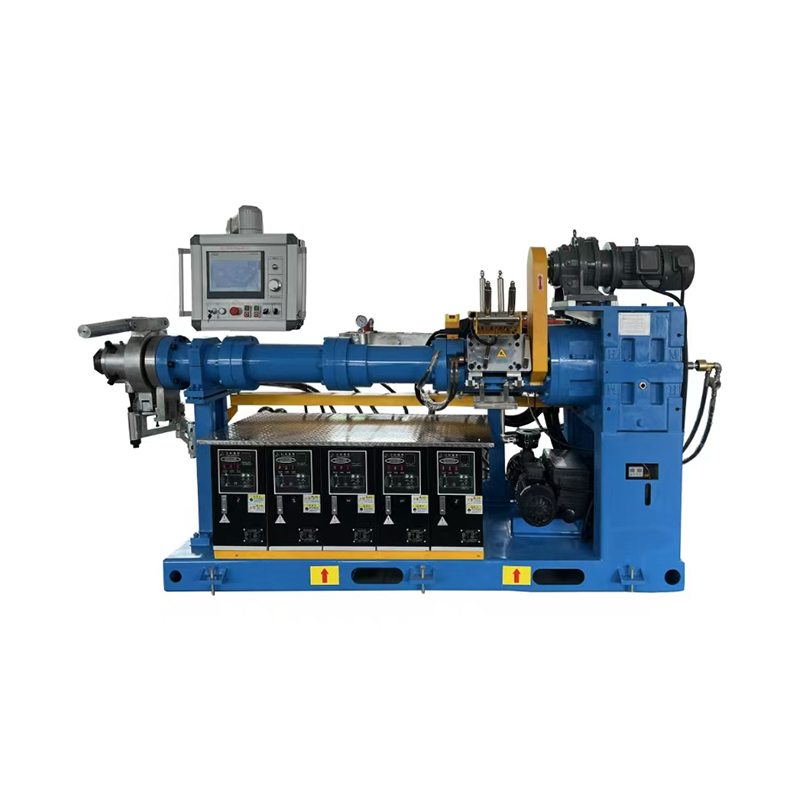
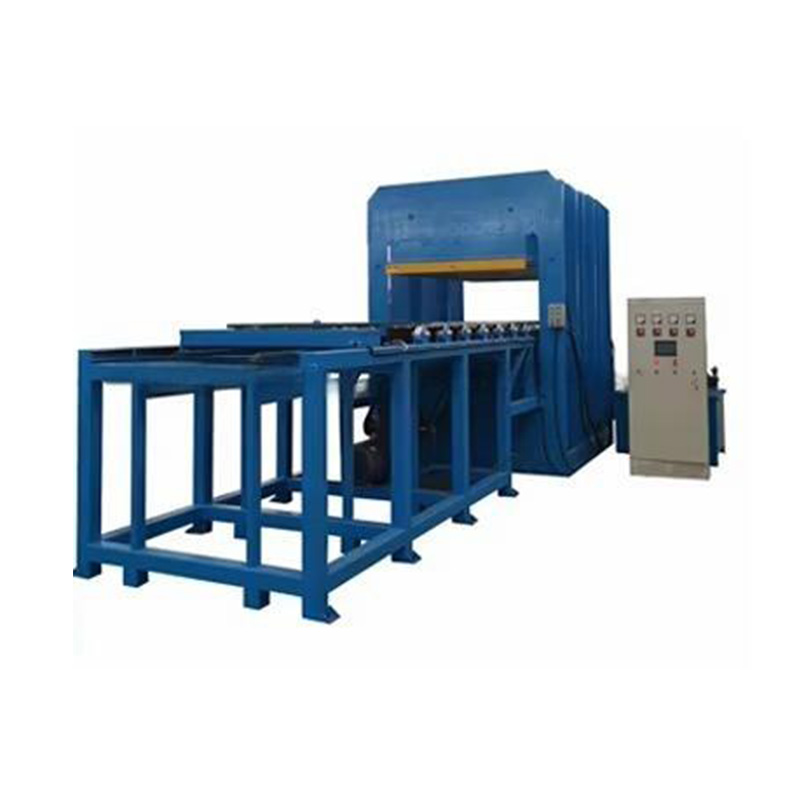
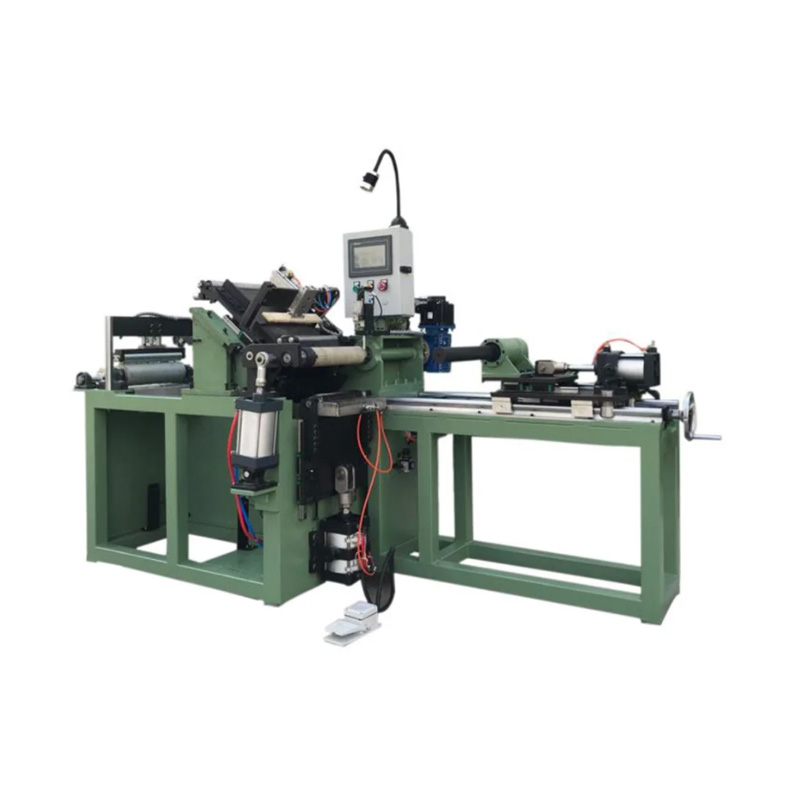
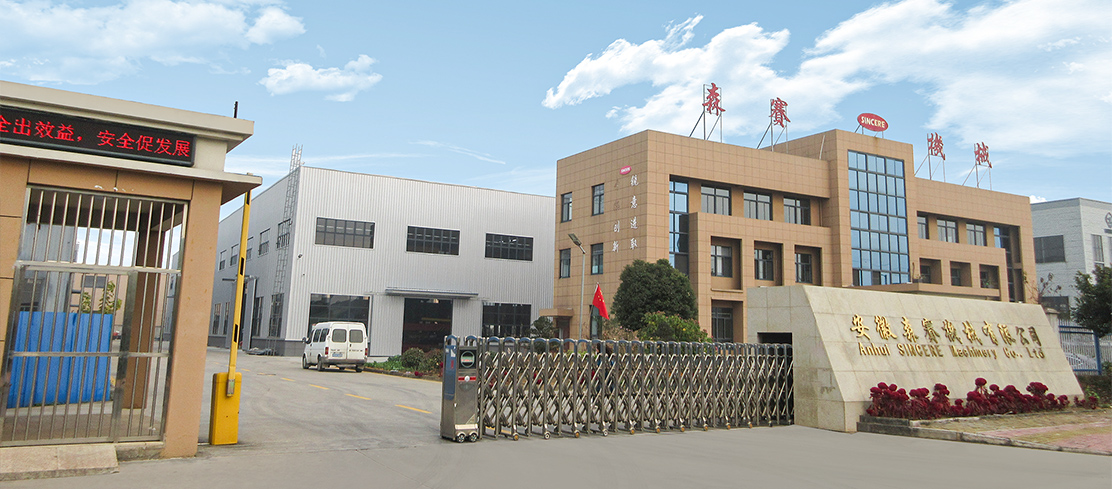
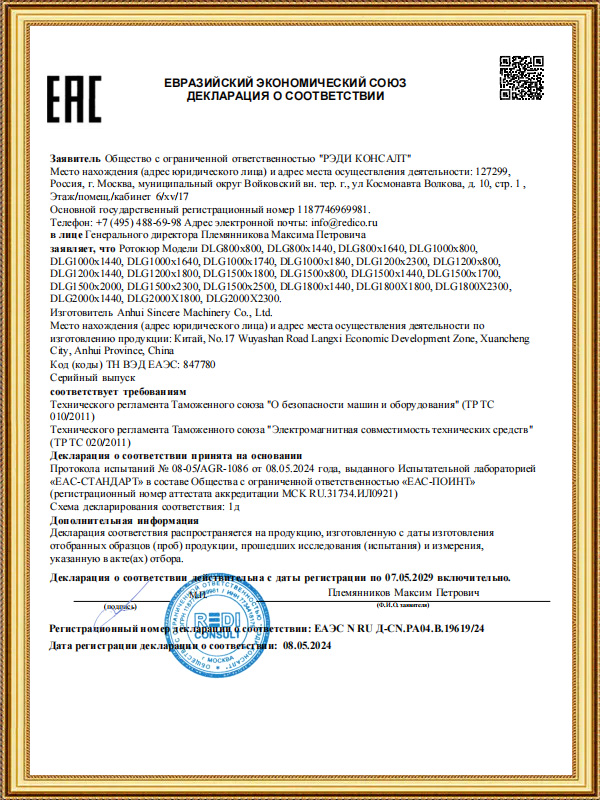
Anhui Sincere Machinery Co., Ltd. founded in 2017, is a comprehensive enterprise specializing in the rubber and plastic machinery industry, integrating R&D, manufacturing and after-sales services. Injection Moulding Machine Suppliers and Injection Moulding Machine Company in China, our factory, spanning nearly 20,000 square meters, is a testament to our robust manufacturing capabilities. We are also equipped to design and manufacture a variety of specialized rubber and plastic machinery to meet the specific requirements of our clients.
We have achieved certifications from SGS and CE, and hold multiple patents for our technologies. Custom Injection Moulding Machine. Our products have earned a stellar reputation in the global market. Our equipment is not only popular in the domestic market but also exported to over 20 countries worldwide, including South Korea, Thailand, and India, extending our brand's influence across the globe.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский