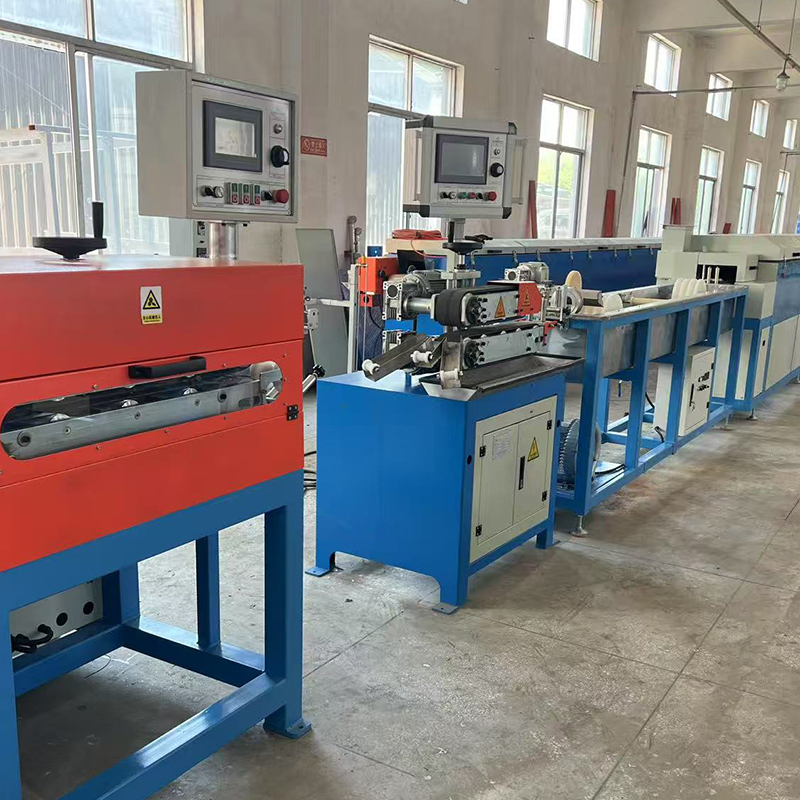
1. Enhancing Extruder Efficiency in Rubber Processing
In modern rubber and plastic machinery, extruder efficiency directly affects product quality and production cost. One practical approach is optimizing the screw design to balance shear rate and residence time. Screws with variable pitch and barrier flights can significantly reduce energy consumption while ensuring consistent mixing of fillers and additives.
Additionally, precise temperature control along the barrel zones is critical. Installing advanced thermal sensors at multiple points allows operators to adjust heating or cooling dynamically, preventing material degradation or incomplete vulcanization. This approach is particularly important for processing heat-sensitive elastomers like EPDM or silicone rubber.
2. Innovations in Injection Molding for Plastics
2.1 Multi-Cavity Mold Cooling Techniques
For high-volume production, uniform cooling across all cavities is essential to minimize warpage and shrinkage. Incorporating conformal cooling channels through 3D-printed mold inserts allows more uniform heat dissipation. Using baffles and inserts made from high-conductivity copper alloys can also reduce cycle times by 10-20% without compromising part quality.
2.2 Injection Pressure Profiling
Fine-tuning injection pressure profiles can improve surface finish and dimensional accuracy. By adjusting the pressure at different stages—initial fill, packing, and hold—manufacturers can prevent sink marks and voids. Pressure profiling is especially valuable for thick or complex geometries, such as automotive interior panels or medical housings.
3. Advanced Mixing Techniques for Rubber Compounds
Effective mixing of rubber compounds is crucial for consistent mechanical properties. Internal mixers with intermeshing rotors are often used for high-viscosity compounds. Optimizing rotor speed, fill factor, and mixing sequence can improve dispersion of carbon black or silica, directly affecting tensile strength and wear resistance.
In addition to mechanical optimization, introducing ultrasonic-assisted mixing has shown promise in reducing processing time while enhancing filler distribution. This method can be particularly useful for specialty rubber compounds used in vibration dampening or sealing applications.
Predictive maintenance using vibration analysis and thermal imaging can prevent unplanned downtime. Regular inspection of bearings, screw flights, and barrel wear is critical for extrusion and injection molding equipment. Implementing IoT sensors to track torque, temperature, and vibration trends allows early detection of abnormal conditions, reducing maintenance costs.
Lubrication management also plays a key role. Using high-performance synthetic lubricants for gearboxes and hydraulic systems improves energy efficiency and extends component life. Keeping a log of lubricant changes and monitoring contamination levels can prevent premature failures and enhance machine reliability.
5. Comparative Table: Screw Types in Plastic and Rubber Extruders
| Screw Type |
Application |
Advantages |
Limitations |
| Single Screw |
Thermoplastics & basic rubbers |
Simple design, easy maintenance |
Limited mixing efficiency |
| Twin Screw |
Compounded rubbers & engineering plastics |
Excellent mixing, high output |
Higher cost, complex maintenance |
| Barrier Screw |
Rubber with fillers |
Improved homogenization |
More sensitive to process parameters |



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский